Refractive Index











Refractive Index
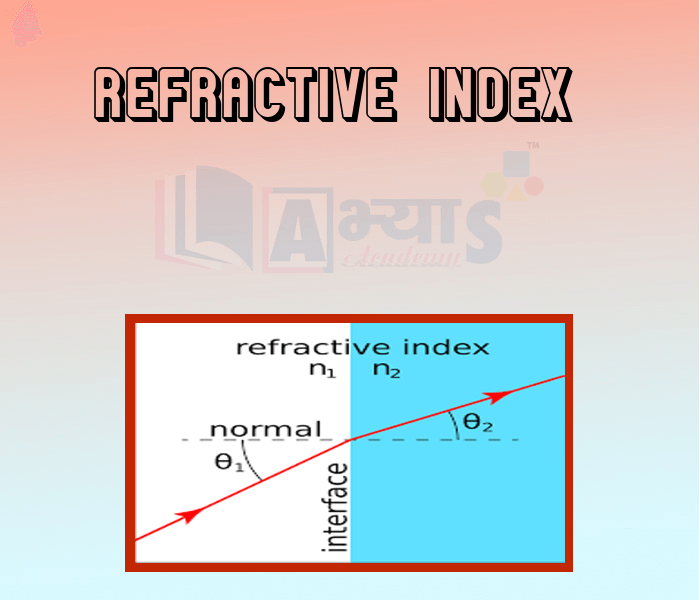
Light travels at a speed of in vacuum. Light travels at different speeds in different materials because as the light enters any material the atoms of the material absorb, scatter and remit light. Therefore, when it travels from one medium to another, the speed either increases or decreases. The amount by which its speed changes determines the amount by which it will change its direction.
The speed of light in vaccum is . The speed of light in a transparent medium such as glass, water or clear plastic is less than this. To calculate the amount by which the ray will deviates from its path we use a physical quantity known as refractive index. It is the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to the speed light in that medium. As the refractive index is a ratio of two same quantities that is speed it does not have any units.
where c = the speed of light in vacuum and v = the speed of light in the medium.
In all material media the speed of light is less than c. Hence, the refractive index of a material medium is greater than 1. The speed of light in air at atmospheric pressure is very close to that in vacuum, and we generally take the refractive index of air as 1.
The refractive index of water is about 1.33, and that of ordinary glass and diamond are about 1.50 and 2.42 respectively.
Larger the refractive index of a medium, greater is the bending of light when it enters the medium from air obliquely. Thus light bends more when it enters a diamond than when it enters an imitation jewel made of glass.
Which of the following is a unit of refractive Index? | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Refraction is the change in the direction of light due to change in ____________of light | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
If the velocity of light in vacuum is | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
I have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.
